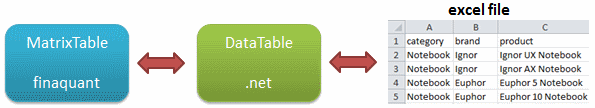
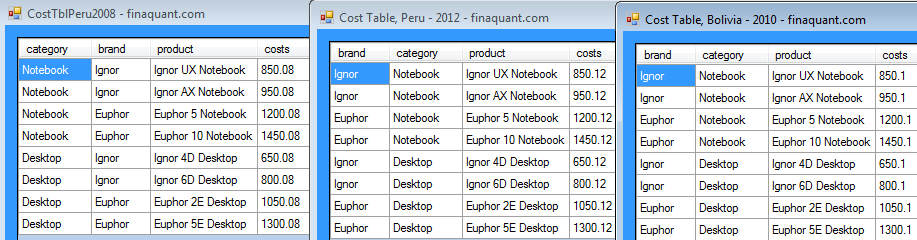
This article explains how the table functions of the non-commercial .net library finaquant® protos can be called from within Microsoft Excel using VBA macros.
Two possible integration options are presented here:
1) Calling a .net method from an Excel macro
Once called from a macro, the .net method reads the input tables from the given excel worksheets before executing the table functions to obtain output tables. The output tables are in turn written into the desired excel sheets.
Note that names of the worksheets are passed from the macro to the .net method as parameters for selecting the input tables. Each worksheet contains a single input table.
This integration option can be useful for demonstrations that are executed directly from excel. See the code examples below:
Excel VBA macro calling .net method: CalculatePrices()' Calculate price table with given cost and margin tables ' 1) Read input tables: Costs, Margins, MetaData ' 2) Calculate price table ' 3) Write resultant price table into a sheet Private Sub CalculatePrices() Dim pxl As New ProtosExcelFunc Dim CostTableSheet, MarginTableSheet, MetaDataSheet, PriceTableSheet As String CostTableSheet = "CostTable" MetaDataSheet = "MetaData" MarginTableSheet = "MarginTable1" PriceTableSheet = "PriceTable1" 'MarginTableSheet = "MarginTable2" 'PriceTableSheet = "PriceTable2" ' call .net method MsgBox pxl.CalculatePrices(Application.ActiveWorkbook.FullName, CostTableSheet, _ MarginTableSheet, MetaDataSheet, PriceTableSheet) End Sub |
/// <summary> /// Calculate price table for given cost and margin tables /// </summary> /// <param name="ExcelFilePath">Full file path of excel file</param> /// <param name="CostTableSheet">Name of worksheet for reading cost table (input table)</param> /// <param name="MarginTableSheet">Name of worksheet for reading margin table (input table)</param> /// <param name="MetaDataSheet">Name of worksheet for reading field names and types (input table)</param> /// <param name="PriceTableSheet">Name of target worksheet for writing price table (output table)</param> /// <returns>Message to calling function</returns> public string CalculatePrices(string ExcelFilePath, string CostTableSheet, string MarginTableSheet, string MetaDataSheet, string PriceTableSheet) { try { // read meta data DataTable MetaTbl = ExcelFunc.ReadTableFromExcelSheet_ODBC(ExcelFilePath, MetaDataSheet); MetaData md = MetaData.ReadFieldsFromDataTable(MetaTbl); // read input tables DataTable CostTbl = ExcelFunc.ReadTableFromExcelSheet_ODBC(ExcelFilePath, CostTableSheet); DataTable MarginTbl = ExcelFunc.ReadTableFromExcelSheet_ODBC(ExcelFilePath, MarginTableSheet); // convert DataTable to MatrixTable MatrixTable CostTable = MatrixTable.Import_from_DataTable(CostTbl, md); MatrixTable MarginTable = MatrixTable.Import_from_DataTable(MarginTbl, md); // Calculate price table with table function 'MultiplySelectedKeyFigures' MatrixTable PriceTable = MatrixTable.MultiplySelectedKeyFigures(CostTable, (MarginTable + 1), InputKeyFigTbl1: "costs", InputKeyFigTbl2: "margin", OutputKeyFig: "price", JokerMatchesAllvalues: true); // convert MatrixTable to DataTable DataTable PriceTbl = MatrixTable.Export_To_DataTable(PriceTable); // write price table into excel sheet ExcelFunc.WriteTableToExcelSheet(PriceTbl, ExcelFilePath, SheetName: PriceTableSheet, SaveWorkbook: false); // return affirmative message to caller return "Price table is calculated successfully!"; } catch (Exception ex) { return "CalculatePrices: An error has occured! " + ex.Message; } } |
2) Directly executing the .net method
… which reads input tables from the given excel file before making the required table calculations.
In this option, an excel sheets are used solely as a database to store input and output tables; no additional VBA code (Excel macro) is needed. See the code example below:
.net code for calculating prices: CalculatePriceTable()/// <summary> /// Calculate price table with given cost and margin tables /// </summary> public static void CalculatePriceTable() { // Get full file path string filepath = System.IO.Path.GetFullPath(@"Resources\DotNetIntegration.xlsm"); // call table function ProtosExcelFunc pxl = new ProtosExcelFunc(); string msg = pxl.CalculatePrices(filepath, CostTableSheet: "CostTable", MarginTableSheet: "MarginTable1", MetaDataSheet: "MetaData", PriceTableSheet: "PriceTable1"); System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine("Message from CalculatePrices: " + msg); } |
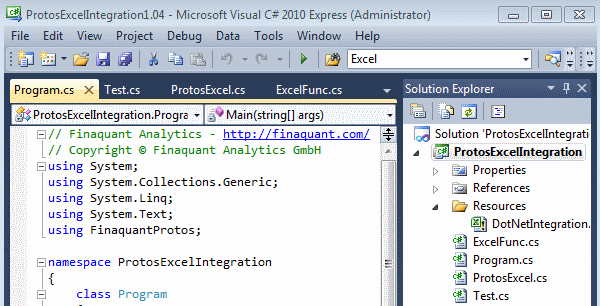
All the example codes above and others can be found in MS Visual Studio File ProtosExcelIntegration (6432 downloads) . Continue reading
 Copyright secured by Digiprove © 2013 Tunc Ali Kütükcüoglu
Copyright secured by Digiprove © 2013 Tunc Ali Kütükcüoglu